Strong bones are essential for overall health, mobility, and a high quality of life. As we age, bone density naturally decreases, making it crucial to maintain both bone and muscle strength to prevent fractures, osteoporosis, and other skeletal issues. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy lifestyle choices play a key role in supporting bone health and muscle strength.
How to Maintain Muscles to Support the Bones
Muscles act as a protective cushion for bones, helping to maintain posture, balance, and movement. To keep muscles strong and supportive:
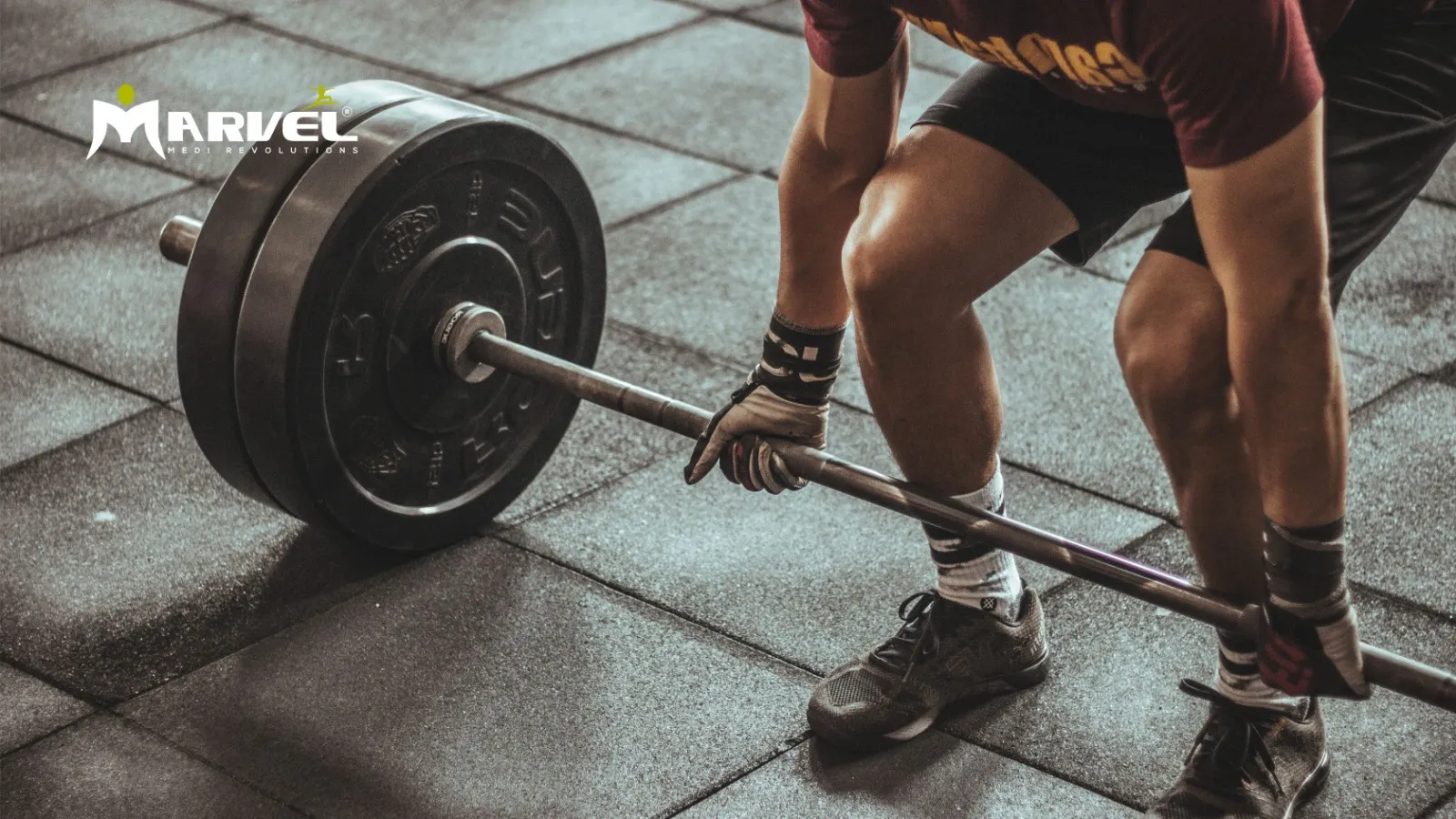
- Strength training (e.g., weight lifting, resistance bands) improves muscle mass and enhances bone density.
- Adequate protein intake supports muscle repair and growth.
- Hydration and balanced electrolytes prevent muscle cramps and weakness.
- Stretching and mobility exercises enhance flexibility and reduce the risk of injuries.
Strengthening the Bones
Bones require essential nutrients and exercise to remain strong.
Key factors include:
- Calcium-rich foods (dairy, leafy greens, tofu, fortified plant-based milk) support bone structure.
- Vitamin D (from sunlight, fatty fish, fortified foods, and supplements) enhances calcium absorption.
- Magnesium and phosphorus contribute to bone density.
- Weight-bearing exercises (walking, jogging, resistance training) stimulate bone growth.
- Muscle Growth and Nutrients for Bone Absorption
- Protein (lean meats, fish, eggs, beans, nuts) aids muscle repair and development.
- Vitamin C (citrus fruits, bell peppers) promotes collagen formation, essential for bone and joint health.
- Vitamin D and calcium work together to strengthen bones and prevent osteoporosis.
Bone Pain Relief and Exercises
- For individuals experiencing bone pain or stiffness, the following strategies can help:
- Low-impact exercises (swimming, yoga, Pilates) ease joint pain while maintaining mobility.
- Stretching and flexibility routines reduce stiffness and improve range of motion.
- Strength training improves joint stability and reduces bone-related discomfort.
- Anti-inflammatory foods (turmeric, ginger, omega-3 fatty acids) help alleviate bone pain.
Conclusion
Maintaining strong bones and muscles requires a combination of proper nutrition, regular exercise, and lifestyle adjustments. A diet rich in calcium, protein, and vitamins D & C, along with strength and weight-bearing exercises, helps prevent bone-related issues and supports lifelong mobility. Small daily efforts in diet and movement contribute to lifelong bone health and overall well-being.