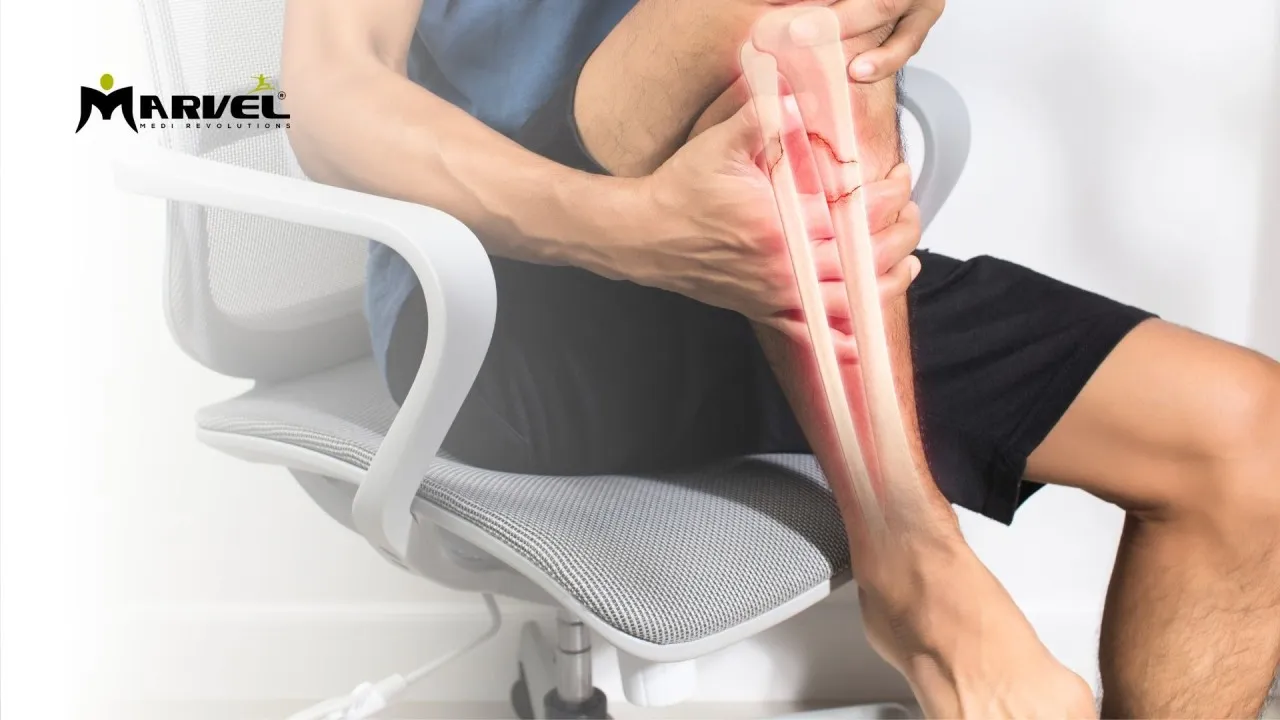
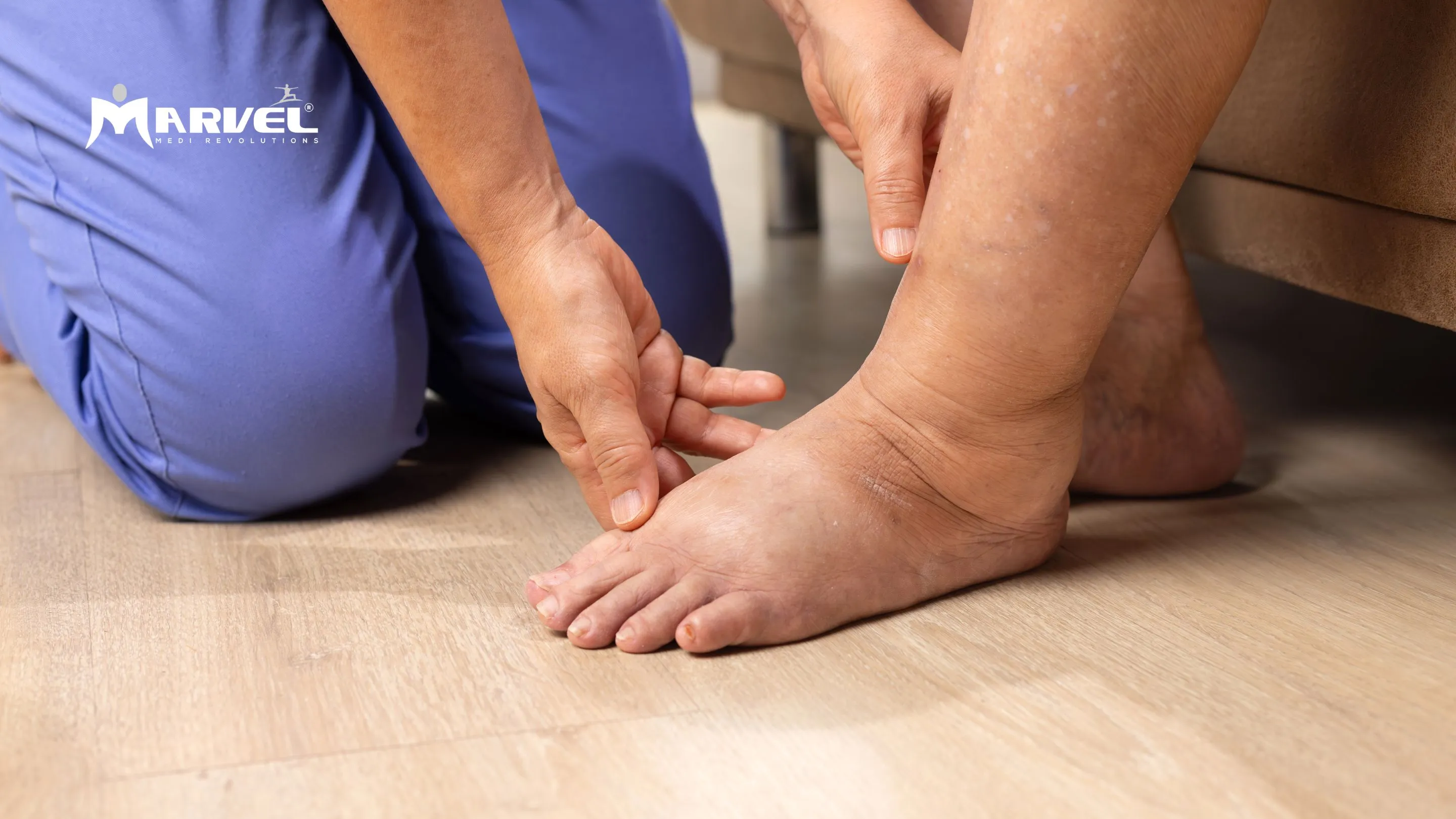
Bone health is crucial for overall well-being, mobility, and independence. Bone damage can result from injuries, aging, nutritional deficiencies, or chronic conditions such as osteoporosis and arthritis. Preventative measures can help maintain strong bones and reduce the risk of fractures and other bone-related issues.
Causes of Bone Damage
Bone damage can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients.
- Aging: Bone density decreases naturally over time.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity weakens bones.
- Chronic Diseases: Conditions like osteoporosis, arthritis, and diabetes can increase the risk of fractures.
- Injuries and Accidents: Falls, fractures, and high-impact injuries can cause bone damage.
- Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, can weaken bones over time.
Preventative Measures
Adequate Nutrition:
- Consume calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, almonds, and fortified foods.
- Ensure sufficient vitamin D intake through sunlight exposure, fatty fish, and fortified foods.
- Include magnesium, phosphorus, and vitamin K in your diet to support bone mineralization.
Regular Exercise:
- Engage in weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, and dancing.
- Perform resistance training exercises to strengthen bones and muscles.
- Practice balance and flexibility exercises such as yoga and tai chi to prevent falls.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as they can weaken bones.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on bones and joints.
- Stay hydrated to support overall bone health and joint function.
Injury Prevention:
- Use protective gear when engaging in high-risk activities or sports.
- Ensure a safe home environment by reducing tripping hazards, using non-slip mats, and installing grab bars in bathrooms.
- Wear supportive footwear to prevent falls and provide stability.
Regular Check-Ups:
- Get bone density tests if you are at risk of osteoporosis or fractures.
- Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice on bone health.
- Monitor and manage chronic conditions that may affect bone health.
Conclusion
Taking proactive steps to maintain bone health is essential to prevent damage and ensure long-term mobility and independence. By incorporating proper nutrition, exercise, and precautionary measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of bone-related issues. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle will further support strong and resilient bones throughout life.